
The most common oxidation state of carbon in inorganic compounds is +4, while +2 is found in carbon monoxide and transition metal carbonyl complexes. They are chemically resistant and require high temperature to react even with oxygen. All carbon allotropes are solids under normal conditions, with graphite being the most thermodynamically stable form at standard temperature and pressure. Under normal conditions, diamond, carbon nanotubes, and graphene have the highest thermal conductivities of all known materials. Graphite is a good electrical conductor while diamond has a low electrical conductivity. Graphite is soft enough to form a streak on paper (hence its name, from the Greek verb "γράφειν" which means "to write"), while diamond is the hardest naturally occurring material known. For example, graphite is opaque and black, while diamond is highly transparent. The physical properties of carbon vary widely with the allotropic form. Well-known allotropes include graphite, diamond, amorphous carbon, and fullerenes. The atoms of carbon can bond together in diverse ways, resulting in various allotropes of carbon. It is the second most abundant element in the human body by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual ability to form polymers at the temperatures commonly encountered on Earth, enables this element to serve as a common element of all known life. Ĭarbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity. Three isotopes occur naturally, 12C and 13C being stable, while 14C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent-its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. Magnesia, a district of Eastern Thessaly in GreeceĪlumina, from Latin alumen (gen.−4, −3, −2, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4 (a mildly acidic oxide)Ĭarbon (from Latin carbo 'coal') is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6.
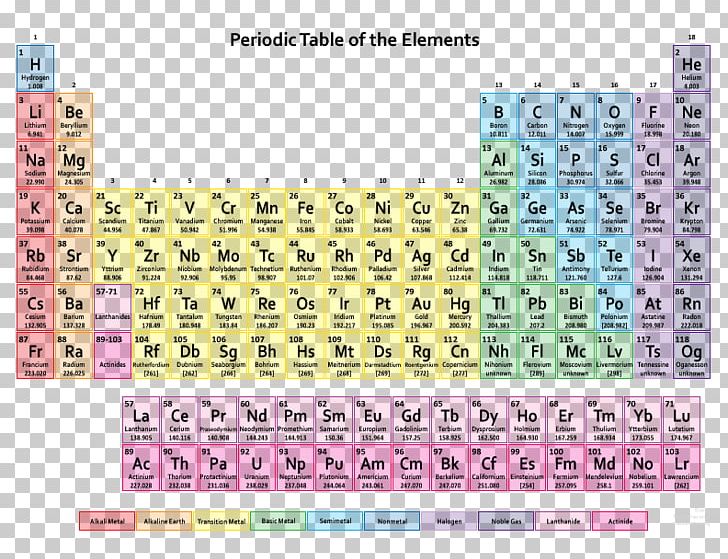
Like the periodic table, the list below organizes the elements by the number of protons in their atoms it can also be organized by other properties, such as atomic weight, density, and electronegativity.
Atomic number c full#
It is a tabular arrangement of the elements by their chemical properties that usually uses abbreviated chemical symbols in place of full element names, but the linear list format presented here is also useful. The definitive visualisation of all 118 elements is the periodic table of the elements, whose history along the principles of the periodic law was one of the founding developments of modern chemistry. A chemical element, often simply called an element, is a type of atom which has the same number of protons in its atomic nucleus (i.e., the same atomic number, or Z). This is a list of the 118 chemical elements that have been identified as of 2023. List of the 118 identified chemical elements


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
